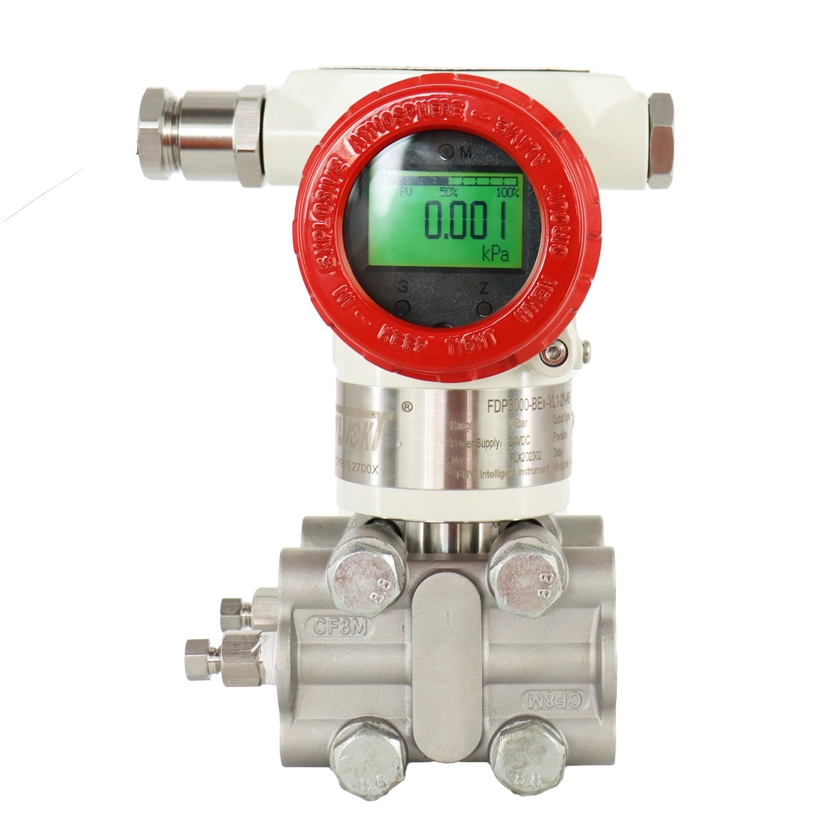
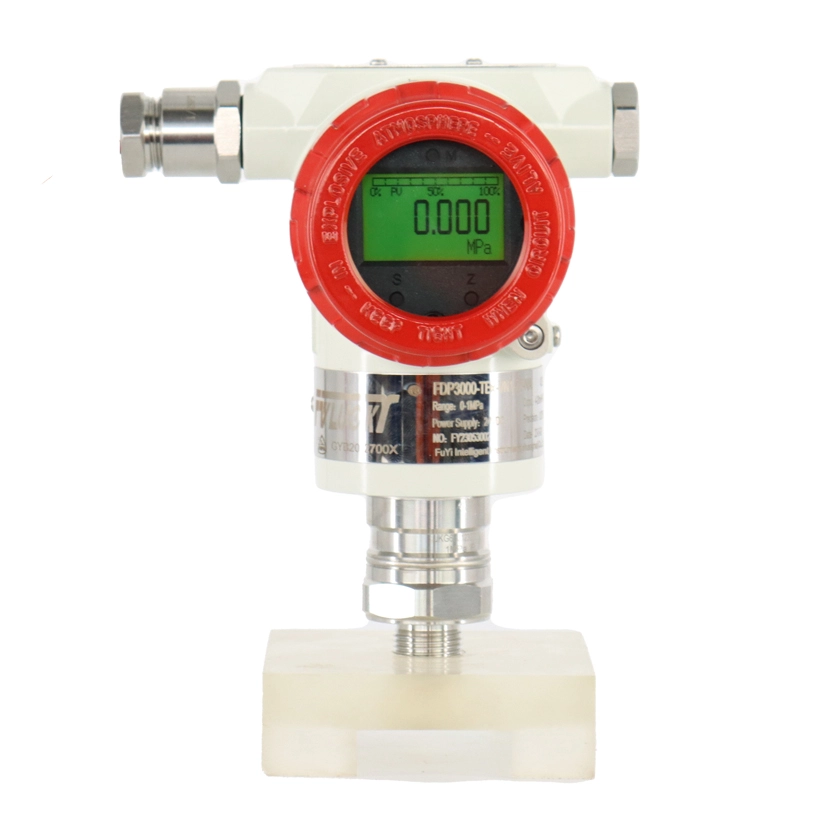
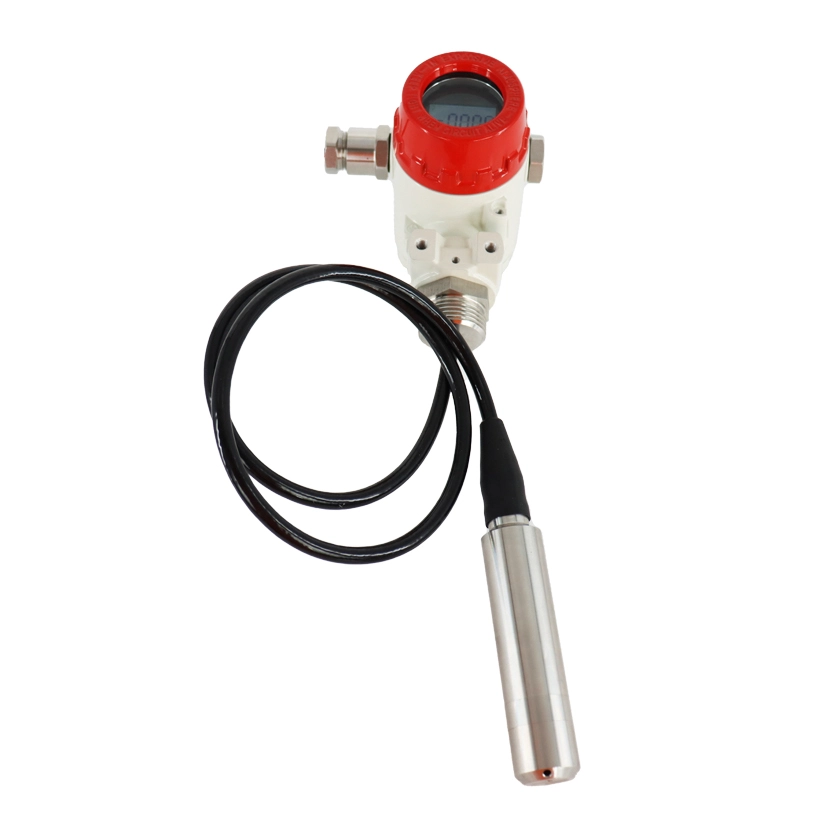
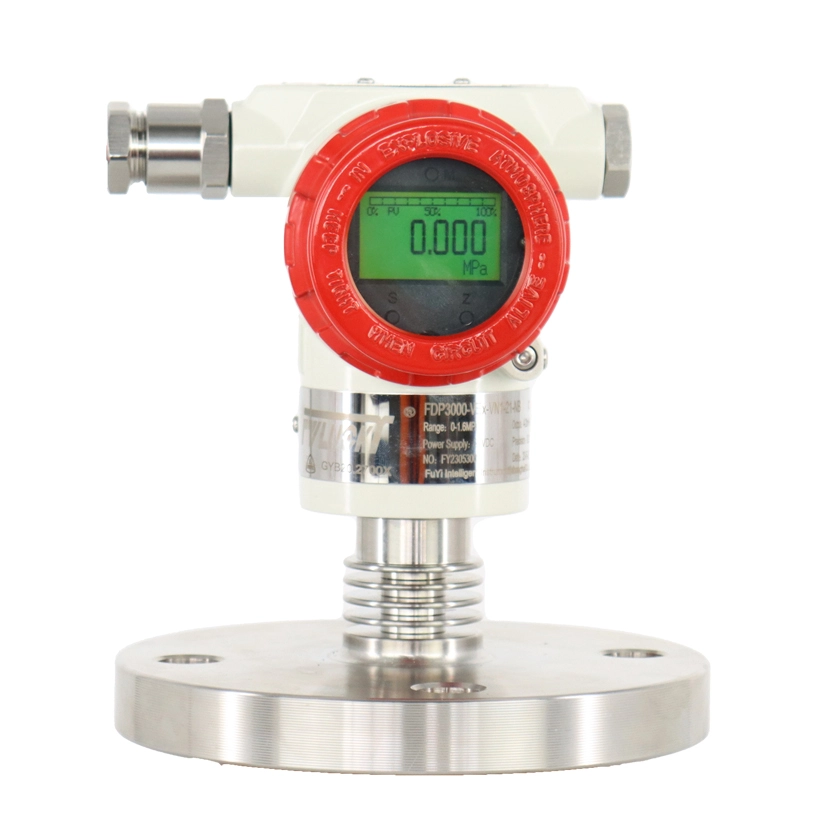
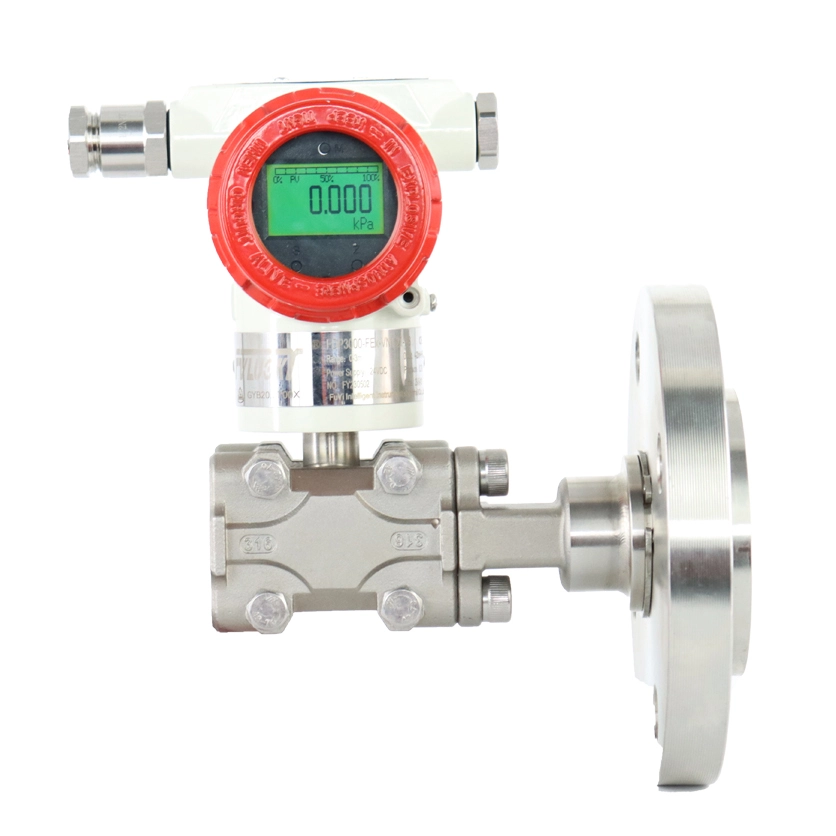
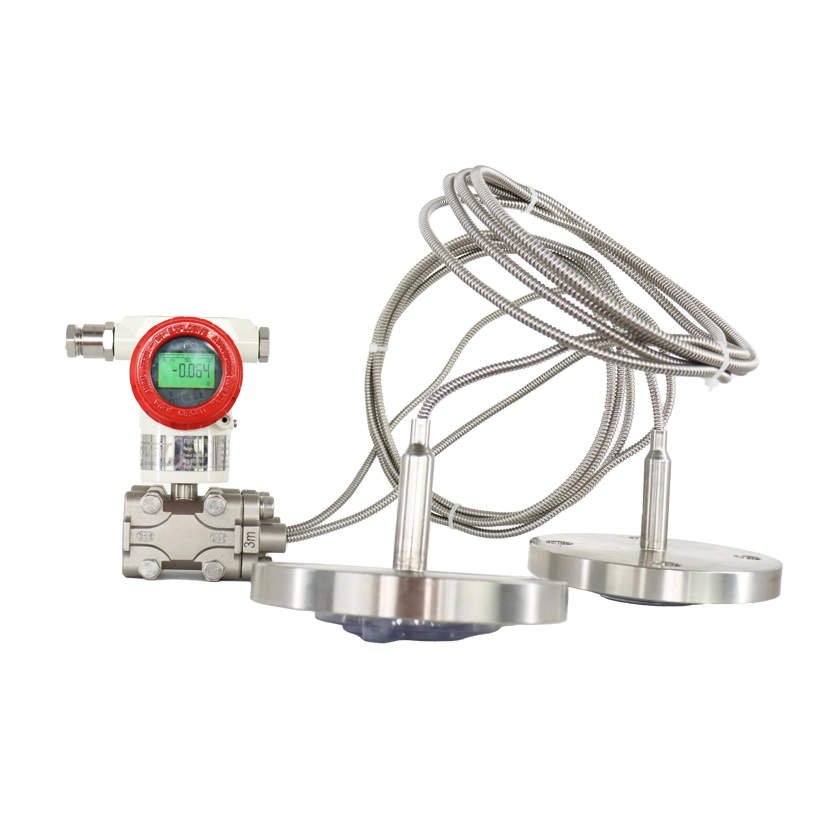
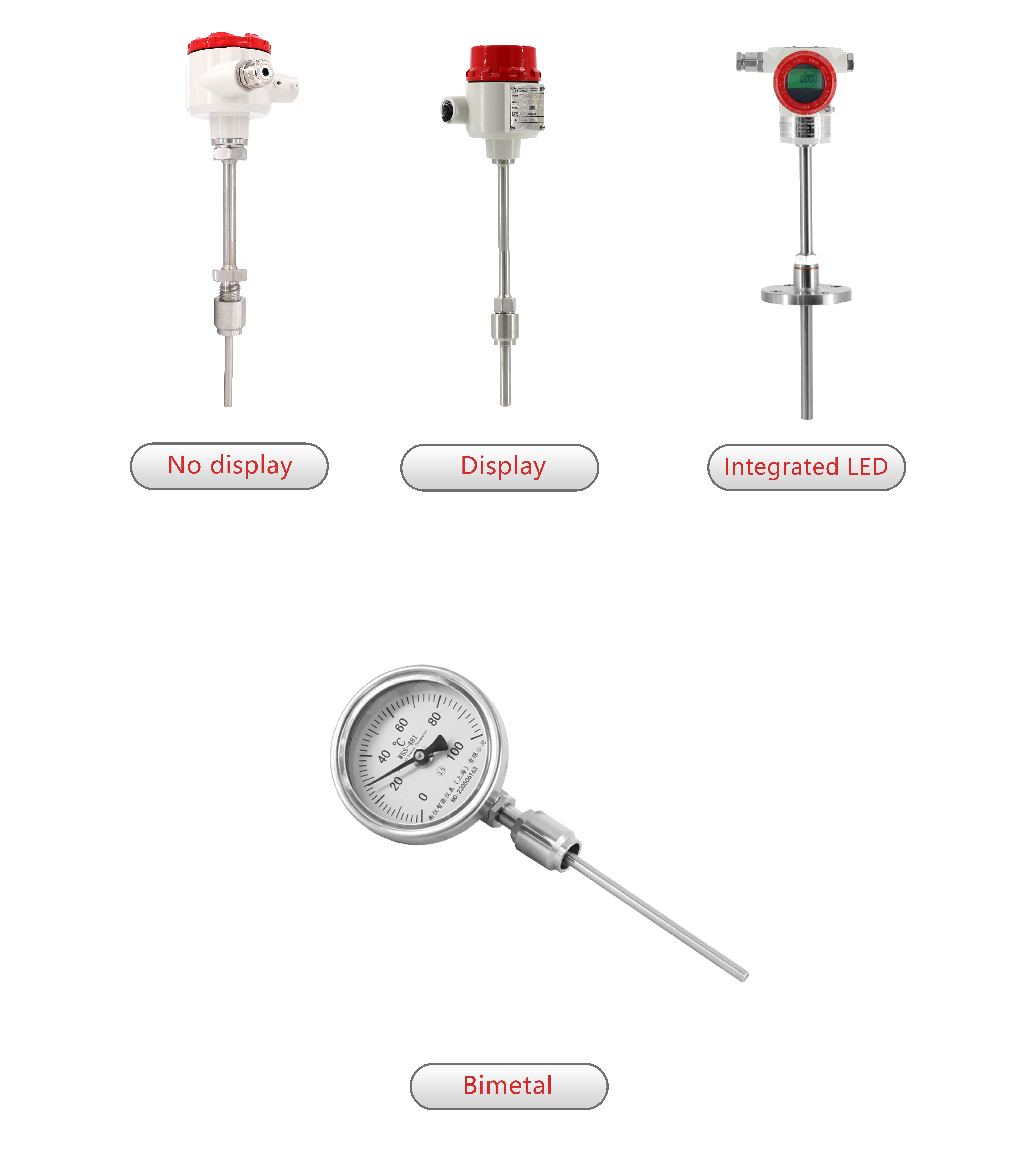
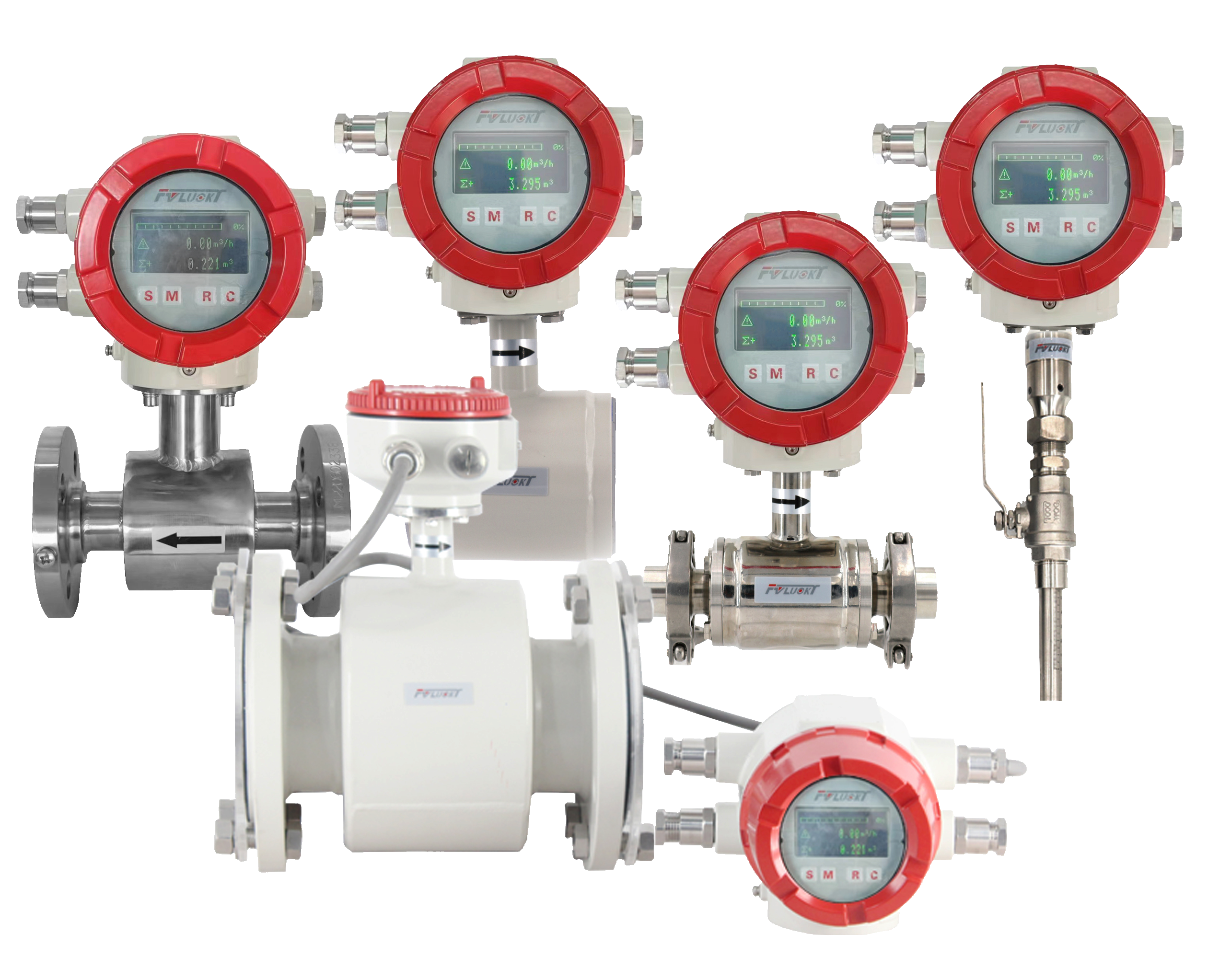
Smart Pressure Transmitters
FvLuoky is one of the best industrial gauge manufacturers, their single-crystal silicon smart pressure transmitter, using original imported chips and packaging technology, enables the smart transmitter to handle the most demanding industrial environment applications. The design of various structures for smart pressure transmitters is sufficient to solve measurements of pressure, differential pressure, liquid level, density, interface, and flow in the industry.
Understanding Smart Pressure Transmitter Working Principle
The smart pressure transmitter is a pressure measuring device that can convert pressure signals into standard electrical signals. The working principle of a smart pressure transducer is mainly to sense the pressure of the measured medium through the pressure-sensitive element, then convert the pressure signal into an electrical signal. This electrical signal of the smart pressure transmitter will be amplified and converted into a digital signal through an analog-to-digital converter. The digital signal is then processed and calculated by a microprocessor, and finally converted into a 4- 20mA current signal output through a digital-to-analog converter. In this process, the microprocessor can also linearize the signal, compensate for temperature, etc., to improve the measurement accuracy and stability of the transmitter. For many process applications, the physical integration is achieved using a threaded pressure transmitter, which ensures the necessary robust, leak-proof, and high-pressure seal required for continuous industrial operation. At the same time, the intelligent smart pressure transmitter also has self-diagnosis and remote communication functions, which can realize real-time monitoring of equipment status and remote parameter setting.
Why Upgrade to a Smart Pressure Transmitter?
So, you're looking at transmitters and wondering what separates a "normal" one from a "smart" one. At their core, both do the same basic job for you: they measure a process variable like pressure and convert it into a standard electrical signal. The real difference, and where the value for your operation lies, is in how they communicate. Think of a conventional transmitter as a one-way street; it reliably sends out a 4-20mA analog signal, constantly reporting "The pressure is X," but it can't listen for any feedback.
A smart pressure transmitter, on the other hand, transforms this monologue into a powerful, two-way dialogue. Using a digital protocol like HART, it sends rich diagnostic and status data over the same two wires you use for the measurement signal. This capability is a game-changer for your team. Smart pressure transmitters mean you can remotely check the device's health, adjust its configuration, or even run a diagnostic test from the control room, saving countless hours of fieldwork and significantly improving safety.
Ultimately, when you're choosing between smart pressure transmitters and normal pressure transmitters, we advise you to consider the application's importance. For a simple, non-critical monitoring task, a normal pressure transmitter is a cost-effective workhorse. But for any process where accuracy, reliability, and uptime are crucial, the smart pressure transmitter becomes your intelligent partner. It actively works to protect your process by alerting you to potential problems before they happen, making it an indispensable tool for modern industrial control.
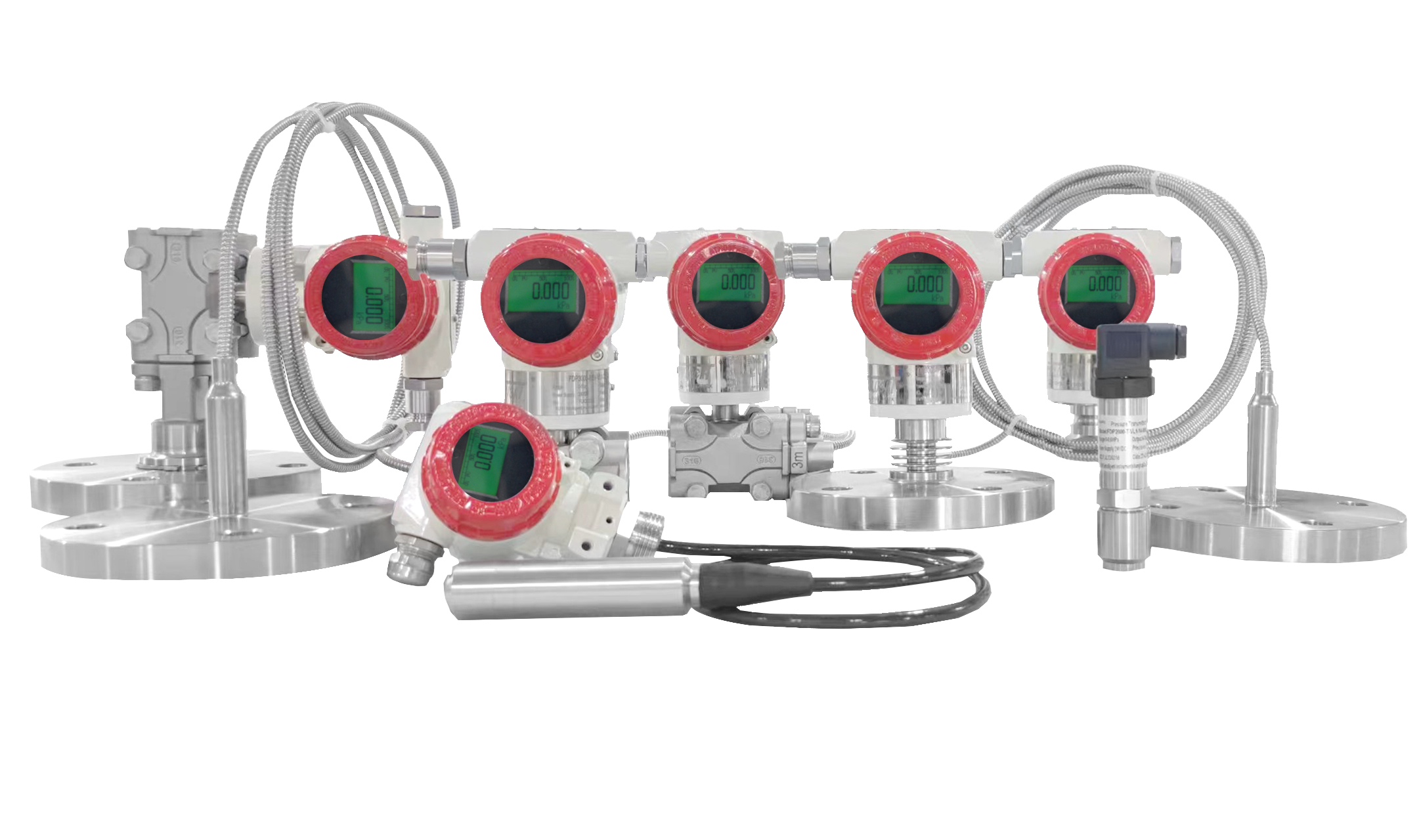
 Smart Pressure Transmitters
Smart Pressure Transmitters